Artificial turf is currently widely used in parks, kindergarten venues, golf courses, and school playgrounds. However, whether or not artificial turf materials are toxic and harmful, and the “heat island effect†on the safety of the active population, has increasingly attracted people’s attention. In this paper, through the investigation of artificial turf in the primary school of Weibin District, combined with the relevant literature and data reports of experts on the artificial turf research, the potential hazards of the artificial turf to the atmosphere and the human body are proposed. The pollution of harmful substances in artificial turf is harmful to the atmosphere. Countries are actively looking for ways to innovate. With the rise of some powerful enterprises with intellectual property rights in China, the quality of artificial turf in China will gradually increase as global integration flourishes. . First, the status of domestic artificial turf The artificial turf was born in the United States in the 1960s. It is a non-living plastic chemical fiber product made from artificial grass. Due to the simple conservation of artificial turf, rapid drainage, and smoothness of the site, artificial turf has been widely used in the recreation and play of children's and adults' pastures, parks, sports venues, and school sports venues. At present, there are more than 20 manufacturers of artificial turfs in the country. From the perspectives of scale, equipment, technology, product quality, and sales ability, only a few are truly capable. Other manufacturers are still in the small factory, non-professional production stage, and even some manufacturers are transformed from the carpet factory. Most of these artificial turf producers are concentrated in the South of China and Shanghai and other regions. Most of them lack brand awareness, lack certain market operation capabilities, lack a very professional management team and technical personnel, and cause domestic quality of artificial turf. Varied, low-grade product proliferation, while domestic low-end industry weaving industry developed, but the core material straw fiber preparation high-end industry gap. Most of the artificial turf used in China depends on imports. Expensive prices can make many schools prohibitive, and some have to buy cheap and inferior products from small workshop manufacturers. Second, the structure of artificial turf Artificial turf consists of 3 layers of material. The basement layer is composed of compacted soil layer, gravel layer and asphalt or concrete layer. Above the base layer is a buffer layer, usually made of rubber or foam. The third layer, also the surface layer, is the turf layer. According to the surface shape of the production of fluffy turf, circular curled nylon silk turf, leaf-shaped polypropylene fiber turf, nylon permeable turf composed of water. III. Hazard identification of toxic and harmful chemical pollutants in turf Artificial turf is composed of a mixture of polyethylene and polypropylene, woven to simulate grass blades. This “grass†is laid vertically, mostly polyethylene (PE) and polypropylene (PP), and polyvinyl chloride and polyamide are also available. The leaves are painted in green that resembles natural grass. Plastics and chemical fiber materials contain a large number of chemicals known or suspected to cause health effects. In order to improve or make up for the performance of plastic materials, manufacturers add more additives to the raw materials by adding additives: imitating the color of natural grass, flame retardancy, high temperature resistance, UV absorbers, structural reinforcement and wear resistance Sex etc. However, these additives, which are so numerous in variety, have become the main harmful factors for the secondary pollution of artificial turf after improving and enhancing certain properties of the materials. The commonly used additives for recycled plastics are: (l) Fillers: Most fillers play a reinforcing role and are also an important part of plastics modification and preparation of composite materials, such as graphite, aluminum disulfide, asbestos fibers, and glass fibers; also known as fillers or fillers. Fillers account for approximately 40% to 70% of the plastic components. Common fillers include wood flour, talc, diatomaceous earth, limestone powder, aluminum powder, carbon black, mica, aluminum disulfide, asbestos, and glass fibers. Among them, fibrous fillers can increase the structural strength of plastics; asbestos fillers can improve the heat resistance of plastics; mica fillers can enhance the electrical insulation of plastics; and graphite and aluminum disulfide fillers can improve the friction and wear resistance of plastics. In addition, since fillers are generally less expensive than synthetic resins, the addition of fillers can reduce the cost of plastics. (2) Curing: Also called hardener or curing agent. Its role is to make the resin have a body-shaped network structure through cross-linking, become a more rigid and stable rubber products, different types of resins should use different types of curing agents. For example, hexamethylenetetramine is added to the phenol resin, and ethylenediamine, maleic anhydride, and the like are added to the epoxy resin. (3) Plasticizer: In order to improve the plasticity of the plastic during processing and the flexibility and elasticity of the product, A small amount of plasticizer should be added during the production and processing of plastic products. Plasticizers are generally solid or liquid organic compounds having a relatively low molecular weight that are not volatile. Mainly lipids and ketones, commonly used dioctyl phthalate, dioctyl phosphate, dimethyl phosphate, adipic acid, benzophenone and so on. For example, the addition of dibutyl phthalate to polyvinyl chloride resin can make the plastic soft and flexible, but studies have shown that it can be used for various organs of experimental animals such as reproductive organs, blood, kidneys, lungs, and liver. Injury, especially in pregnant women and developmental children, is very sensitive to its toxic effects. (4) Stabilizers: artificial turf in the process of molding and processing, due to the role of heat, photo-oxygen, premature degradation, oxidation broken chain, cross-linking and other phenomena, so that the performance of the material deteriorated. In order to prevent the effect of heat, light, etc., to make the plastic fiber prematurely aging and adding a small amount of substances that can stabilize, for example, adding organic substances such as phenols and amines can resist oxidation, and carbon ink can be used as an ultraviolet absorber; Heat stabilizers are the most commonly used additives in plastic products other than plasticizers. In general, epoxidized seed oils or vegetable oils such as soybean oil (ESBO) and the like are widely used as heat stabilizers, lubricants, and plasticizers for plastic food packaging materials. Polyvinyl chloride, polyvinylidene chloride, and polystyrene materials usually contain 0.1 to 27% of epoxidized vegetable oil. Since the residual ethylene oxide in vegetable oil is extremely toxic, the purity of the oil will directly affect its degree of toxicity. In general, the greater the molecular weight (ie, the lower the solubility), the weaker the toxicity. (5) Flame retardant: The role is to prevent combustion or cause self-extinguishing, more mature flame retardants include inorganic materials such as yttrium oxide, or phosphoric acid and organic compounds such as oxo compounds. (6) Colorants: Colorants may be added to give plastic products a specific color and luster. Colorants are classified into dyes and pigments according to their solubility in a coloring medium. The dyes are all organic compounds and can be dissolved in pigmented resins; pigments are generally inorganic compounds and are insoluble in the coloring medium. Their coloring properties are dispersed in the dyed medium through their own highly dispersed particles, and their refractive index is different from the matrix. Large, absorbs part of the light, and reflects another part of the light, giving people the vision of color. Pigments not only have a coloring effect on plastics, but also have the function of fillers and stabilizers. In addition, lubricants, antistatic agents, foaming agents, flame retardants, and mildewproofing agents may be added depending on the needs of the use of plastics in construction and molding processing. The artificial grass turf regenerated plastic fiber is used as an example to analyze possible harmful factors in the main components of recycled plastic fibers. The sources of raw materials for the production of plastic fibers are extremely complex, inevitably containing polyvinyl chloride components, or containing other unknown poisons and a large number of microorganisms that are invisible to the naked eye. During the processing of raw materials, plasticizers and plastic stabilizing agents such as lead stearate are added. In the production process, recycled plastic fibers are added with colorants in order to cover up many raw material impurities. Therefore, various kinds of colorful lawns are common. Its permeability, volatility, when exposed to oil, hot, easy to seep out. If it is an organic colorant, it also contains benzopyrene carcinogens, which can cause stomach cancer, colon cancer, etc. Some inorganic calcium minerals and talcum powder are added to the production of recycled plastics. The evaporation residue of health indicators is greatly exceeded. Students are When you eat it while eating, you can easily develop cholelithiasis after entering the body. Some recycled plastics have a pungent odor that releases the toxic gas HCl, which enters the human body to form a hazard. In summary, the main pollution factors of recycled plastic fibers and their harm to the human body and the environment are shown in Table 1. Plastic fiber and rubber particle main pollution factor Harm to the environment and human body Curing agent (hexamethylene tetramine, ethylene diamine, maleic anhydride, etc.) Hexamethylenetetramine mainly causes dermatitis and eczema. Plasticizers (dibutyl phthalate, etc.) Irritating to skin and mucous membranes, mild sensitization. Contact can cause multiple neuritis, spinal neuritis and cranial neuritis, allergic rhinitis, dermatitis and gastroenteritis, nausea, dizziness and toxic nephritis caused by misuse. Stabilizers (lead stearate, etc.) Lead compound health hazards: manifested as headache, insomnia, forgetfulness, and excitability, especially in children, may have ADHD, and severely affect intellectual development, interfere with the synthesis of hemoglobin, in severe cases, anemia, loss of appetite, constipation Abdominal pain, hepatomegaly, tenderness and renal hypertension can occur. In particular, it has a great influence on the fetus, which can cause miscarriage, fetal abnormalities, and so on. For men, there are symptoms of sexual dysfunction and sperm reduction. Sodium Compound Health Hazards: The motor system exhibits muscle pain in the lower extremities, pain after stressing the bones, and osteoporosis. Cough, difficulty breathing, pneumonia, pulmonary edema. Causes chronic interstitial nephritis, chronic renal failure, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, olfactory disturbances, disturbed sleep, and prostration. Flame Retardants (Oxide, Phosphoric Acid, and Brominated Compounds Continuously entering and accumulating in the human body through the food chain will lead to developmental toxic neurological effects, such as changes in spontaneous consciousness, impairment of learning ability and memory capacity, and also affect the brain development and hormonal balance of infants. It may have the same consequences. Toxic gases (HCl, etc.) Eye and respiratory mucosa have a strong stimulating effect. Acute poisoning: headache, dizziness, nausea, eye pain, cough, sputum blood, hoarseness, difficulty breathing, chest tightness, chest pain. Severe cases of pneumonia, pulmonary edema, corneal ulcers or turbidity. Direct contact with the skin can occur with a large number of miliary red papules and hot flashes. Chronic effects: Long-term exposure to higher concentrations can cause chronic bronchitis, gastrointestinal dysfunction, and tooth erosion. Colorants (such as benzopyrene, etc.) Strong carcinogens can cause stomach cancer, colon cancer, etc. Other unknown poisons and microorganisms, germs The artificial turf serves as a mat by adding a layer of rubber particles having a diameter of 3 mm or less made of recycled tires. Sometimes the rubber particles are mixed with silica sand as a filler. Fourth, the rubber particle filler hazard identification The most common synthetic rubbers are composed primarily of ethylene-propylene and styrene-butadiene, with different levels of vulcanizing agents, fillers, plasticizers, and antioxidants. Different manufacturers add different formulations. Tire rubber also contains polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), phthalates, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). After combustion, rubber may produce CO, SO2, H2S, HCN, NO2, HCI, arsenic, cadmium, lead, nickel, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, and volatile organic compounds. Some studies have shown that these chemicals are released in large amounts when the rubber burns, and they can be slowly released during the aging of the rubber particles. The California Environmental Health Hazard Assessment Office (OEHHA) reported in its January 2007 report entitled “Evaluation of the Health Effects of Used Waste Tires for Sports Fields and Athletic Tracks†that the tire rubber particles release 49 chemicals. Based on an experiment simulating the digestion of gastric juice, OEHHA estimated that the risk of one-time ingestion of rubber particles from a person with a tumor is 1.2 millionths of a millionth, well below the minimum risk threshold of one millionth. In a hands-on experiment, OEHHA estimated that the risk of developing cancer was increased by exposure to rubber granule fillers via hand and mouth and ingestion of 1,2-benzopyrene (a suspected human carcinogen found in tire rubber). 2.9 parts per million. This estimate is based on the assumption of the first 12 years of service life in a conventional stadium. The author believes that the risk of cancer is "slightly higher than the minimum level." In the summer of 2007, the Connecticut Environment and Human Health Corporation commissioned a study at the Connecticut Agricultural Experiment Station to determine whether toxic substances in rubber particles could be released into the air or water. In the report “Artificial Turf†(Artificial Turf), a total of 25 chemicals were detected by mass spectrometry-gas chromatography, and the determinacy was 72 to 99%. Compounds that must be included include the stimulants benzothiazole and n-hexadecane, carcinogens, and suspected endocrine disruptors tert-butyl p-hydroxyanisole and etchant, a corrosive that can damage the mucosa. Artificial turf fillers are tiny rubber particles that can be airborne, inhaled, and can be carried into the home with clothing and sports equipment. For adults, the tiny, black, rubber particles are at best annoying. But children will not have any harm when exposed to these fillers. Patti Wood, executive director of the non-profit grassroots environmental education organization, said: "Because of its toxicity, disposal of such rubber particles in landfills or marine dumping areas is illegal. How can we allow children to play on them? †In summary, the main pollution factors of rubber particles and their harm to the human body and the environment are shown in Table 2. Rubber particle main contamination factor Harm to the environment and human body Alkanes, aromatic hydrocarbons Alkanes: Vapors have anesthetic and expectorant effects; Aromatic hydrocarbons: Carcinogenic effects. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons The main hazards to the human body are the respiratory tract and the skin. Common symptoms include solar dermatitis, acne dermatitis, folliculitis, and verrucous organisms. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) fall on the leaves of plants, blocking the leaves' breathing holes, causing them to discolor, shrink, curl, and fall off, affecting normal plant growth and results. Sulfur compounds (H2S, mercaptans, and SO) H2S: through the respiratory tract into the body, easy to cause poisoning; mercaptans: mainly in the central nervous system, inhalation of low concentrations can cause headache nausea, high concentrations cause respiratory paralysis and death; SO: a strong stimulating effect on the eyes and respiratory mucosa, A large amount of inhalation can cause pulmonary edema, laryngeal edema, and vocal cord paralysis. CO Into the body soon after combined with hemoglobin, increased tissue hypoxia, leading to hypoxemia, causing brain hypoxia and cerebral edema, but also induced cardiovascular disease. NO2 It mainly acts on the deep respiratory tract, bronchioles, and alveoli, causing irritation and corrosion to the lung tissue and causing pulmonary edema. particulates After entering the respiratory tract, it can stimulate and erode the respiratory mucosa and lung cells, reduce the respiratory defense function, increase the incidence of respiratory tract, and even increase the mortality rate. Artificial turf may affect the surrounding considerable ecosystem during use. After artificial turf has been exposed to the sun, rain, and wind, harmful substances in the turf have dissolved from plastics and rubber, and natural rain, such as rain, has penetrated into the soil, causing pollution to the soil. Its pollution to the soil includes changing the physical structure and chemical properties of the soil, affecting plant nutrient absorption and growth, affecting the activity of microorganisms in the soil, destroying the ecological balance within the soil, and accumulating harmful substances in the soil, resulting in excess of harmful substances in the soil. , impede the growth of plants, and even cause death of plants in severe cases. The enzyme in the soil and the plants closely related to the soil are used as the main evaluation receptors. By measuring the activity changes of different enzymes in the soil and the growth and development of the plants growing in the soil, the renewable polyethylene waste plastic resources are measured in chemical products. Pollutants are mainly heavy metals, including lead, cadmium, chromium, arsenic, etc. Among them, the lead concentration of heavy metals is the highest, and the impact is greatest. Harmful substances can also be absorbed by plants, transferred to fruit, affect human health and feeding animals through the food chain; in addition, germs carried by recycled building materials can also spread diseases and cause biohazards to the environment. The EHHI project studied whether artificial turf fields would increase water pollution through rain or water spray. The study found that 25 kinds of chemicals and 4 kinds of metals (zinc, selenium, lead and cadmium) in rubber packing can be released into water, and because artificial turf cannot absorb or filter rainwater, chemicals have not been effectively filtered by vegetation. Hazardous substances flow into the rivers and lakes with natural precipitation, causing surface water pollution. As the permeated water enters the soil and the groundwater is contaminated and flows directly into lakes, rivers, or oceans, it will cause a greater area of ​​water pollution. The main component of artificial turf is non-biodegradable material. After being aged out by 8 to 10 years, it forms tons of polymer waste. Therefore, this waste material must be properly disposed of. Rick Doyle, chairman of the Artificial Turf Committee, said that the filler can be cleaned and reused for other uses, such as rubber asphalt, incineration, spread over the soil to separate the soil from landfill waste, or recycled. In reality, however, abandoned artificial turf is usually buried. Sixth, the "heat island effect" of artificial turf The turf bed structure of artificial turf is composed of rubber, concrete or asphalt, which can not basically play a role in conserving water sources. Therefore, the surface temperature cannot be reduced, and its heat capacity is small, resulting in a surface temperature significantly higher than the air temperature, especially in closed stadiums. This issue is even more serious. At noon of summer, the artificial turf field can observe the obvious heat distortion of the air near the surface. The experimental data show that under the high temperature conditions above 30°C, the average surface temperature of natural turf is lower than the temperature of 2°C to 3°C, while the surface temperature of artificial turf is higher than the temperature of 6°C to 11°C and increases with the temperature. The increase in surface temperature of artificial turf is significantly higher than that of natural turf. Stuart Gaffin, an associate research fellow at Columbia University's Climate Systems Research Center, began his research on temperature issues in the artificial turf playing field as he conducted studies on urban cool trees and parks. Using thermal infrared satellite imagery and geographic information systems, Gaffin found that many of the hottest places in the city are artificial turf fields. Direct temperature measurement data from field studies show that the temperature of artificial turf fields can be 60°F higher than that of natural turf, and the surface temperature in summer can reach 160°F. For example, on July 6th, 2007, the air temperature was 78°F at noon, and the temperature of natural grass that was directly exposed to the sun was 85°F, while the temperature of the adjacent artificial grass sports field reached 140°F. Many of the physical properties of artificial turf, including melanin, low-density mass, cannot vaporize water to reduce the ambient air temperature, allowing it to rapidly increase in temperature when exposed to the sun. This is not only harmful to people who are active on the sports field, but also exacerbates the "heat island effect" - because black artificial surfaces (such as roofs and asphalt) can absorb heat, causing the city to be hotter than the surrounding areas. Through multiple on-site investigations of black roofs and artificial turf fields, Gaffin believes that artificial turf is comparable to black roofs in raising surface temperatures. Joel Formans, medical director of the Children's Environmental Hygiene Task Force at Mount Sinai School of Medicine, said: “It takes more than 10 minutes at temperatures above 122°F to cause skin damage, so this issue really needs attention.†Seventh, artificial turf can hide more bacteria Most bacteria in the air are not harmful to humans, but there are also some pathogens that can spread to the surrounding environment, causing allergic reactions in humans and causing serious health hazards to people with low immunity. These bacteria may include hemolytic streptococci, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, pneumococcus and other pathogenic microorganisms. Poor ventilation in the gaps in the artificial turf, high air humidity, bacteria can maintain a longer survival time and pathogenicity. In order to understand the bacteria distribution and species composition of artificial turf, we tested the distribution of bacteria in different places of artificial turf track, basketball court and flag raising platform in some schools in January 2003. Materials and Method 1, medium Nutrient agar medium, and enrichment medium, separation medium, preservation medium, physiological and biochemical reagents, and sterile water. 2, instruments and identification cards VITEK- 32 automatic microbiological analyzer, Gram-negative bacteria identification card (GNI), rapid Gram-negative bacteria identification card (GNI), Gram-positive bacteria identification card (GPI), 3, sampling points From January 7 to January 10, 2013, the total number of turf fungi was monitored at 3 sampling sites in 6 schools. 4, sampling method The natural sedimentation method was used to take the nutrient agar medium to take the sampling point for 5 min and place it in a 37°C biological incubator. After 48 hours of culture, the total number of colonies in the petri dish was directly counted. The total number of air bacteria was 15/dish for evaluation. The qualified rate of monitoring the total number of bacteria in the flag-raising station in Taichung is very high, and the pass rate of the runway and basketball court is relatively low. This shows that there is a long time between activities, intense sports, and frequent student activities. place Number of samples Qualified copies Pass rate track 12 2 16% Basketball court 10 3 30% Flag station 11 7 64% There are 6 identified bacteria in the sampled artificial turf, of which there are more Gram-positive bacteria (about 72.5%) and Gram-negative bacteria (about 32.6%), of which the dominant bacteria are Micrococcus, Bacillus, Pseudomonas, and Staphylococcus species accounted for 33.5.0%, 24%, 17.5%, and 15.9%, respectively, of the total bacteria, which is consistent with the species of pathogenic bacteria that cause respiratory infections. Species track Basketball court Flag station average Gram-positive bacteria 71. 77.3 79.5 60.7 72.5 Bacillus 26.3 28.7 17 twenty four Micrococcus 37.6 38.8 twenty four 33.5 Staphylococcus 1 19.7 16 12 15.9 Microbacterium 3.5 2.7 1.7 2.6 Gram-negative bacteria 28. 33 35.7 29 32.6 Pseudomonas 18.8 19.7 14 17.5 Alcaligenes 9.6 8.8 7.3 Unidentified 7.9 6 8 place Number of samples Qualified copies Pass rate track 12 2 16% Basketball court 10 3 30% Flag station 11 7 64% An industrial study funded by artificial turf manufacturer Sprinturf found that the amount of bacteria in fillers containing sand and rubber mixtures was 50,000 times higher than that of pure rubber fillers. These pathogenic bacteria can be brought into the air along with the wind of dust and student movements, causing inhalant allergic mildew. Patient chest tightness, cough, fever, fatigue, joint pain and so on. This poses a great threat to the physical health of physical education teachers who lead student activities in artificial turf for more than three hours a day. Conclusion Based on the above, it can be seen that the toxic and harmful substances of cheap artificial turf are one of the important factors that cause campus environment and student safety problems. At present, people around the world are paying more and more attention to the problem of environmental pollution to the human body. Volatilization of harmful substances in inexpensive artificial turf cannot be ignored. The European companies are also looking for innovative solutions to the concerns of artificial turf fillers. For example, Italy is trying to promote artificial turf with non-toxic new thermoplastic materials as fillers in the market. ECOFILL, which is produced by a flooring company, MONDO, is a special technology polyhydrogen granule that is dedicated to artificial turf. The company claims that this material is more heat-efficient, free of polyvinyl chloride, ethylene, plasticizers, heavy metals and other harmful substances, and can be recycled 100%. Another alternative is to make the filler from the material of the plant material. In recent years, countries have increasingly stricter standards for the quality and safety of artificial turf. FIFA has put forward the certification standard for the artificial turf soccer field, the “FIFA Recommended Markâ€. FIFA recommendations are only awarded to artificial turf pitches that pass a series of rigorous laboratory and field tests, not just monoliths. Therefore, manufacturers must first pass laboratory tests, including product identification, durability, and durability. Sex, player (or ball) and turf surface interaction performance testing. After passing these tests, field tests were conducted on all paved football fields, including site structure tests and the interaction of test players (or balls) with turf surfaces. Since FIFA promoted the certification of the quality of artificial turfgrass, 106 of the 270 member countries in six regions in the world have been certified for the construction of 106 sites. The number of venues in the 6 districts of the Football Association that have received FIFA recommendation 2 stars and FIFA recommendations for 1 star certification are listed in the table below. area FIFA Recommend 2 Stars FIFA Recommend 1 Star Europe (UEFA) 19 52 Asia (AFC) 0 19 Oceania (OFC) 0 0 Africa (CAF) 1 2 North America (CONCACAF) 0 8 South America (CONMEBOL) 4 1 It can be seen from the table that the number of certified artificial turf fields in Europe is the most and the highest level; only 19 sites in Asia have passed the 1-star level certification, and China has not yet passed the FIFA quality certification site. With the development of China's artificial turf industry, we believe that companies that are striving for excellence will actively apply for FIFA quality certification, and look forward to the concept of FIFA quality, to curb the phenomenon of China's artificial turf industry. Happy growth under the sky. Baking Molds,Silicone Baking Molds,Silicone Cake Molds,Mini Cake Pans Yangjiang Teammade Industrial Co., Ltd , https://www.yadokitchen.com


Table 1 Main pollution factors and hazards of plastic fibers and rubber particles
Ethylenediamine has strong irritation to mucous membranes and skin. It can easily cause conjunctivitis, bronchitis, pneumonia or pulmonary edema, and can cause contact dermatitis. It can cause liver and kidney damage. Skin and eye can directly contact the liquid and cause burns. , Can also cause occupational asthma.
Maleic anhydride dust and vapors are irritating and can cause pharyngitis, laryngitis, and bronchitis after inhalation. It can be accompanied by abdominal pain. Eyes and skin can cause significant irritation and cause burns. Chronic effects: chronic conjunctivitis, nasal mucosal ulceration and inflammation. Sensitization can cause rashes and asthma. 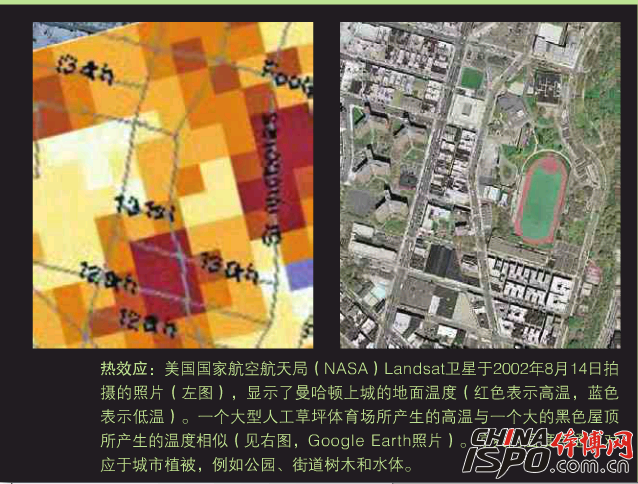

School Artificial Turf Harm Study and Identification
Table 2 The main pollution factors of rubber particles and its harm to human body and environment
V. Hazards Identification of Soil and Plants from Artificial Turf Total number of bacteria in different places of artificial turf
Artificial turf bacterial species composition (%)
Total number of bacteria in different places of artificial turf
The number and distribution of venues for quality certification