[Name] The Republic of Austria [Area] 83871 square kilometers. (Source: Austria Statistical Yearbook 2005) [population] 8.118 million (2003). Among them, 711,000 were foreigners, accounting for 8.8%. Ethnic minorities are Slovenians, Croats and Hungarians, accounting for about 0.52% of the population. The official language is German. 73% of residents believe in Catholicism. [Capital] Wien, population 1.59 million (2003). [Head of State] President Heinz Fischer, elected on April 25, 2004 and assumed office on July 8. [profiles] Landlocked countries located in southern central Europe. It borders Slovakia and Hungary to the east, Slovenia and Italy to the south, Switzerland and Liechtenstein to the west, and Germany and Czech to the north. It is a temperate broad-leaved forest climate with a transition from continental to continental. The average temperature is -2°C in January and 19°C in July. In 996 AD, the first mention of "Austria" was made in history. In the middle of the 12th century, during the reign of the Abbey of Babenberg, it became the Principality and became an independent country. In 1278, the Habsburg dynasty began its 640-year reign. In the early 18th century, the territory of the Habsburg dynasty was unprecedentedly expanded. After the Vienna Conference in 1815, the German Confederation led by Austria was established. In 1866, the Confederacy failed and the Confederacy was dissolved. In 1867, he signed with Hungary and established the Austro-Hungarian Empire. After the end of the First World War in 1918, the Empire disintegrated and established the Republic. March 1938 was annexed by Hitler's Germany. After World War II was occupied by the four countries of the Soviet Union, the United States, Britain and France. The second republic was established in April 1945. In May 1955, the four occupying powers signed the "Austria State Treaty for the Reconstruction of Independence and Democracy" with Austria and announced that they respected the sovereignty and independence of Austria. Occupation forces withdrew in October and Austria regained independence. On October 26, the Austrian National Assembly passed permanent permanent legislation and declared that it would not participate in any military alliance and would not allow the establishment of foreign military bases on its territory. Since October 1965, October 26th has been designated as the Olympic Day. [Politics] In 2005, the Austrian People’s Party-Liberal Party coalition government basically remained stable. The government further deepened adjustments in economics, politics, and society, and introduced a series of measures to promote employment, streamline institutions, increase efficiency, promote growth, reduce unemployment, and reduce the burden on businesses and individuals. Passed the new "Refugee Law" and "Nationality Law" to strengthen the examination of foreigners' naturalization applications. The pattern of political parties continued to change, and the public opinion support rate of the Social Democratic Party in the Federation steadily rose. The Liberal Party’s internal control led to the split. The leader of the party, Haider, led the party’s backbone to announce that he would set up a new hill and set up a new party named “Austrian Future Alliance†and be himself the chairman of the party. The members of the Liberal Party cabinet in the coalition government and most of the party’s members in the National Assembly have joined the New Party “Future Alliance†and continue to co-govern with the People’s Party. The Liberal Party tried to regroup, but there is no obvious result. The Green Party continued to adjust its tactics and adopted a pragmatic policy. The support rate was relatively stable. [Constitution] The current constitution came into force on November 10, 1920. Two by-laws were adopted in 1925 and 1929. The 1934 Constitution was abolished. After the reconstruction of Austria in 1945, the 1920 Constitution and two by-laws were declared valid. According to the constitution, Austria is a federal republic, and the president is the head of state. It is elected by universal suffrage for a six-year term. The prime minister is the head of government. The "Parliament" consists of the National Assembly and the Federal Parliament. The National Assembly enacted laws, presided over the inauguration ceremony of the new government, and dismissed the federal government and its members through a vote of no confidence. The Federal Parliament has the right to reject the legal proposals passed by the National Assembly on behalf of the states. However, if the National Assembly insists on the original case, the Federal Council must not raise objections. The National Assembly has a total of 183 seats. The proportional representation system has been created for a four-year term. This session of the National Assembly came into being in November 2002. The seats occupied by the parties were: the People’s Party 79 seats, the Social Democratic Party 69 seats, the Liberal Party 18 seats, and the Green Party 17 seats. The Speaker of the House of Governors has a term of four years and is currently chaired by Andreas Kohl (People’s Party). There are 62 seats in the Federal Assembly. Each state is selected according to the proportion of its population. The Speaker is elected by the majority of the members of each state in turn and serves for six months. The National Assembly and the Federal Parliament form a federation meeting. Its main function is to accept the President’s oath of office and decide on the need for external declaration of war. [Government] On February 28, 2003, the People's Party and the Liberal Party once again formed a joint cabinet. The current government is composed of the following: Chancellor Wolfgang Schüssel (PPP), Deputy Prime Minister and Minister of Transport, Innovation and Technology Hubert Gorbach (Liberal Party), Foreign Minister Usulah Pou Ursula Plassnik, female, BJP, Minister of Economy, Labour Martin Bartenstein, People’s Party, Finance Minister Karl-Heinz Grasser, non-partisan, interior Minister Liese Prokop (female, People’s Party), Minister of Defence Günther Platter (Poplov), Minister of Justice Dieter Boehmdorfer (without parties), agriculture, forestry and Environmental Minister Joseph Pröll (Poplov), Minister of Social Security Herbert Haupt (Liberty), Minister of Education, Science and Culture Elizabeth Gehrer (female, People’s Party) ), Minister of Health, Family and Youth, Maria Rauch-Kallat (People's Party). [Administrative Division] The country is divided into 9 states: Burgenland, Carinthia, Upper Austria, Lower Austria, Salzburg, Styria, Tyrol, Vorarlberg, and Vienna. Below the state is located city, district, town (township). [Judiciary] There are three court systems across the country: the Constitutional Court, which hears cases concerning disputes between the Constitution, especially local and federal governments, and the President Karl Korinek; the Administrative Court, which deals with official bodies and their staff. The case of administrative disputes was courtesy of Dean Clemens Jabloner; the Supreme Court, hearing criminal and civil cases, Dean Johann Rzeszut. [Party] (1) Austrian People's Party (?sterreichische Volkspartei): the ruling party. The predecessor was the Christian Socialist Party established in 1887 and changed its current name in 1945. Chairman Wolfgang Schüssel. (2) Austrian Future Union (BZ?). ruling party. April 4, 2005 was established because of a split within the Liberal Party. Chairman of the party, Järg Haider. (3) Austrian Social Democratic Party (Sozialdemokratische Partei?sterreichs): opposition parties. Established in 1889. Ruling from 1919 to 1920, banned in 1934. In 1945, it was renamed the Socialist Party. In June 1991, it changed its name. Chairman Alfred Gusenbauer. (4) The Austrian Liberal Party (Freiheitliche Partei?sterreichs): The opposition party. Founded in 1955, the predecessor was the "Independence Alliance", which formed a coalition government with the Socialist Party in 1983-1986. President Heinz-Christian Strach. (4) The Green Party (DieGrünen): The opposition party. The main organizations are "Green Choice" and "Joint Green Party." The federal spokesperson (chairman) Alexandervander Bellen (Alexandervander Bellen). (5) Liberales Forum: opposition parties outside parliament. In February 1993, five former Liberal Party members were established and a national organization was established in November. Federal Spokesperson (Chairman) Alexander Zach. (6) Kommunistische Partei?sterreichs: opposition parties outside parliament. Established in 1918. Implement collective leadership. Federal Council General Secretary Walter Baier. [important figures] Heinz Fischer: President. Born on October 9, 1938 in Graz. In 1971, he was elected member of the National Assembly. Since 1975, he has served as chairman of the Social Democratic Party’s parliamentary group and federal research minister, and was elected president of the National Assembly three times in 1990, 1996 and 1999. He served as the second speaker of the National Assembly in December 2002. He was elected as the Federal President on April 25, 2004 and assumed office on July 8. He visited China several times before he was elected president. Wolfgang Schüssel: Prime Minister. Born in Vienna in June 1945, he graduated from the University of Vienna with a doctorate in law. From 1968 to 1975, he served as Secretary of the National Assembly People's Party Parliamentary Party Committee, from 1975 to 1991 as Secretary General of the People's Party Economic Union, from 1979 to 1989 as Member of the National Assembly, and from 1987 to 1989 as Vice Chairman of the National Assembly People’s Party Parliamentary Party Group, 1995 He served as chairman of the Austrian People’s Party. Since 1989, he has served as Federal Minister of Economy, Deputy Prime Minister and Minister of Foreign Affairs of the Federation. He served as Federal Prime Minister in February 2000 and re-elected in February 2003. He visited China in 1995, 1998, and 2005. [Economy] The main economic figures for 2004 are as follows: Economic growth rate is 1.9% Gross domestic product: 231.8 billion euros. Per capita GDP: 28,700,000 Euros. Gross domestic product growth rate: 2.1%. National income: 197.09 billion euros. Inflation rate: 1.8%. Currency name: EURO, 1 EUR = 100 points. The unemployment rate is 4.2%. Exchange Rates (February 2006): 1 Euro = 1.1752 USD. [Resources] Minerals mainly include graphite, magnesium, lignite, iron, petroleum, and natural gas. Rich in forest and water resources. The forest coverage rate is 42%, there are 4 million hectares of forest farms, and timber reserves are about 990 million cubic meters. [industry] In 2003, the industrial output value was 90.901 billion euros, accounting for 33% of the gross domestic product. The main industrial sectors include chemical, mining, steel, machinery manufacturing, electronics and automotive engine manufacturing. In 2003, there were 415,000 industrial employees. The output of major industrial products is as follows (unit: 10,000 tons): 200120022003 Iron ore 184.3194.2212.5 Oil 105103.2101.5 Natural gas (100 million cubic meters) 19.520.120.3 (Source: Austria Statistical Yearbook 2005) [Agroforestry] In 2003, the output value of agro-forestry was 5.68 billion euros, accounting for 2% of the GDP. The number of agro-forestry employees is 214,000, accounting for 5.1% of the total number of employees. Arable land accounts for 18% of the country's total area, and ranch accounts for 27%. The agriculture is advanced, the degree of mechanization is high, and the agricultural products are more than self-sufficient. The output of major agricultural products is as follows (unit: 10,000 tons): 200120022003 Wheat and rye 172.8160.5132.3 Maize 49.3166.7145.2 Potato 69.568.456.0 Beet 277.3304.3248.5 Number of pigs and cows (in thousands of heads): 200120022003 Pig 344330.5324.5 Cattle 211.8206.7205.2 (Source: Ibid.) [Tourism] Tourism is developed. In 2003, 28.13 million tourists were received, of which 19.08 million were foreign tourists. There are 70019 hotels in the country with a total of 1.032 million beds. The main tourist destinations are Tyrol, Salzburg, Carinthia, Styria and Vienna. Tourists mainly come from Germany, Holland, Sweden, Britain, Belgium and Luxembourg. [Transportation] Austria is located in central Europe and is an important transportation hub in Europe. The traffic conditions in recent years are as follows: Railways: In 2003, the total length of the national railway was 5,656 kilometers, with a passenger volume of 183.7 million passengers and a freight volume of 8,697,000 tons. Highways: In 2003, the total length of all types of highways in the country was about 110,000 kilometers, of which highways and expressways were about 1,900 kilometers. Water transport: Inland river route is 350 kilometers long. In 2002, there were 331 passenger ships and 142 cargo ships. In 2003, the Danube River had 10.737 million tons of cargo. Air Freight: Austrian Airlines, Tyrol Airlines and Lauda Airlines jointly formed the AUA Group, which has 101 aircraft and flies to 130 cities in 66 countries. There are six airports and the main international airport is Vienna Schwechat Airport. [Financial Finance] The financial revenue and expenditure in 2001-2003 are as follows (in millions of euros): 200120022003 Expenditure 604618614 Income 590594579 Deficit 142435 In 2003, national debt was 146.33 billion euros, which was equivalent to 64.7% of GDP. (Source: Austria Federal Ministry of Finance website) [Foreign trade] Foreign trade plays an important role in the economy. With more than 150 countries and regions have trade relations. The foreign trade situation in recent years is as follows (Unit: 100 million euros): 200120022003 Import amount 111211041001 Export volume 111111521091 Difference -14890 (Source: Austria Statistical Yearbook 2005) The main export products are steel, machinery, transportation, chemical products and food. Imports are mainly energy, raw materials and consumer goods. Germany, Italy and Switzerland were the three largest Austrian trading partners in 2003. The film has excellent heat sealing performance and excellent transparency, is one of the main packaging composite base materials, used in the production of high-temperature boiling film, vacuum aluminum coating film, the market is very optimistic.Moreover, with the development of domestic production equipment, some of the technical indicators have reached the international advanced level.As a result, the threshold to enter the film production is lower and lower.Because of this, some enterprises rush to import the flow of film production line in order to reach the designated position, the higher the level, the better, while leaving the market demand and the return on investment aside, which will cause huge waste of resources. Tri-layer Lamination,Viscose PE Film Spunbond Fabric,Spunlace Spunbond Fabric,PE Film Laminated Nonwoven Fabric,Absorbent Lamination XINLE HUABAO MEDICAL PRODUCTS CO.,LTD. , https://www.huabaomedical.com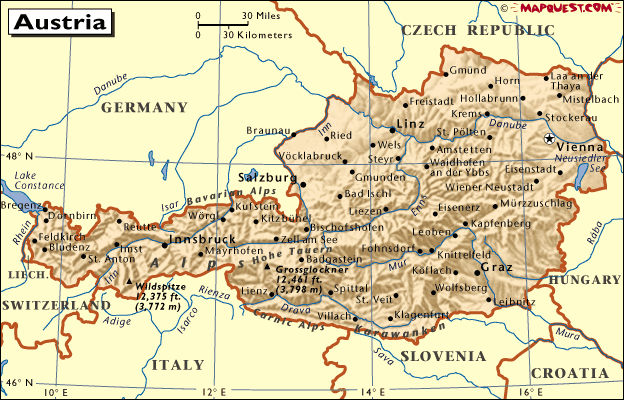
New Edition - Map of Austria and Austria
Welcome to the new 2010 map system: http://
Faster, more maps